Platform paper social experiment analysis: Part 1#
In this guide we will work with data collected from experiments social0.2 and social0.4, in which two mice foraged for food in the habitat with three foraging patches whose reward rates changed dynamically over time.
The experiments each consist of three periods:
“presocial”, in which each mouse was in the habitat alone for 3-4 days.
“social”, in which both mice were in the habitat together for 2 weeks.
“postsocial”, in which each mouse was in the habitat alone again for 3-4 days.
The goal of the experiments was to understand how the mice’s behaviour changes as they learn to forage for food in the habitat, and how their behaviour differs between solo and social settings.
The full datasets are available on the Datasets page, but for the purpose of this guide, we will be using the precomputed Platform paper social analysis datasets.
See also
DataJoint pipeline: Computing behavioural bouts for examples of how we precompute these datasets.
“Extended Data Fig. 7”, in “Extended Data” in the “Supplementary Material” of the platform paper for a detailed description of the experiments.
Below is a brief explanation of how the environment (i.e. patch properties) changed over blocks (60–180 minute periods of time):
Every block begins at a random interval \(t\):
\[ t \sim \mathrm{Uniform}(60,\,180) \quad \text{In minutes} \]At the start of each block, sample a row from the predefined matrix \(\lambda_{\mathrm{set}}\):
\[\begin{split} \lambda_{\mathrm{set}} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 5 & 5 & 5 \\ 1 & 3 & 5 \\ 1 & 5 & 3 \\ 3 & 1 & 5 \\ 3 & 5 & 1 \\ 5 & 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 3 & 1 \\ \end{pmatrix} \quad \text{In meters} \end{split}\]Assign the sampled row to specific patch means \(\lambda_{\mathrm{1}}, \lambda_{\mathrm{2}}, \lambda_{\mathrm{3}}\) and apply a constant offset \(c\) to all thresholds:
\[\begin{split} \begin{aligned} \lambda_{\mathrm{1}}, \lambda_{\mathrm{2}}, \lambda_{\mathrm{3}} &\sim \mathrm{Uniform}(\lambda_{\mathrm{set}}) \\ c &= 0.75 \end{aligned} \quad \text{Patch means and offset} \end{split}\]Sample a value from each of \(P_{\mathrm{1}}, P_{\mathrm{2}}, P_{\mathrm{3}}\) as the initial threshold for the respective patch. Whenever a patch reaches its threshold, resample a new value from its corresponding distribution:
\[\begin{split} \begin{aligned} P_{\mathrm{1}} &= c + \mathrm{Exp}(1/\lambda_{\mathrm{1}}) \\ P_{\mathrm{2}} &= c + \mathrm{Exp}(1/\lambda_{\mathrm{2}}) \\ P_{\mathrm{3}} &= c + \mathrm{Exp}(1/\lambda_{\mathrm{3}}) \end{aligned} \quad \text{Patch distributions} \end{split}\]
Set up environment#
Create and activate a virtual environment named social-analysis using uv.
uv venv aeon-social-analysis --python ">=3.11"
source aeon-social-analysis/bin/activate # Unix
.\aeon-social-analysis\Scripts\activate # Windows
Install the required dependencies.
uv pip install matplotlib numpy pandas seaborn statsmodels pyyaml pyarrow tqdm scipy jupyter
Import libraries and define variables and helper functions#
import math
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Tuple
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import statsmodels.api as sm
from scipy.stats import binomtest, ttest_rel, wilcoxon
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
The hidden cells below define helper functions, constants, and setup variables used throughout the notebook. They must be run, but are hidden for readability.
# CHANGE THIS TO THE PATH WHERE
# YOUR LOCAL DATASET (PARQUET FILES) IS STORED
data_dir = Path("")
Dominance#
Using position and orientation data from multi-animal tracking of pose and identity, we identify social encounters and retreats. These events form the basis of the automated tube test: by considering all automatically scored encounters and retreats, we infer hierarchical relationships across experiments, producing continuous, time-resolved rankings from the most subordinate to the most dominant subjects.
Load data#
social_retreat_df_all_exps = []
social_fight_df_all_exps = []
social_patchinfo_df_all_exps = []
social_patch_df_all_exps = []
pbar = tqdm(
experiments,
desc="Loading experiments",
unit="experiment",
)
for exp in pbar:
data = load_experiment_data(
experiment=exp,
data_dir=data_dir,
periods=["social"],
data_types=["retreat", "fight", "patchinfo", "patch"],
# trim_days=1 # Optional: trim
)
df_retreat = data["social_retreat"]
df_fight = data["social_fight"]
social_patchinfo_df = data["social_patchinfo"]
social_patch_df = data["social_patch"]
df_retreat["experiment_name"] = exp["name"]
df_fight["experiment_name"] = exp["name"]
social_retreat_df_all_exps.append(df_retreat)
social_fight_df_all_exps.append(df_fight)
social_patchinfo_df_all_exps.append(social_patchinfo_df)
social_patch_df_all_exps.append(social_patch_df)
social_retreat_df_all_exps = pd.concat(social_retreat_df_all_exps, ignore_index=True)
social_fight_df_all_exps = pd.concat(social_fight_df_all_exps, ignore_index=True)
social_patchinfo_df_all_exps = pd.concat(
social_patchinfo_df_all_exps, ignore_index=True
)
social_patch_df_all_exps = pd.concat(social_patch_df_all_exps, ignore_index=True)
Fights and retreats#
# Build lookup of social_start & compute per-exp offset to align at earliest start-time
exp_df = pd.DataFrame(experiments)
exp_df["social_start"] = pd.to_datetime(exp_df["social_start"])
exp_df["tod_sec"] = (
exp_df["social_start"].dt.hour * 3600
+ exp_df["social_start"].dt.minute * 60
+ exp_df["social_start"].dt.second
)
# Earliest start-time (seconds since midnight)
min_tod = exp_df["tod_sec"].min()
# Offset seconds so each experiment’s Day 0 lines up at min_tod
exp_df["offset_sec"] = exp_df["tod_sec"] - min_tod
# Compute absolute baseline timestamp per experiment
exp_df["baseline_ts"] = exp_df["social_start"] - pd.to_timedelta(
exp_df["offset_sec"], unit="s"
)
exp_df = exp_df[["name", "baseline_ts"]]
# Print aligned Day 0 hour (earliest start-time)
aligned_hour = min_tod // 3600
print(f"Aligned Day 0 starts at hour {aligned_hour}")
# Compute global end time across both datasets
all_events = pd.concat(
[
social_fight_df_all_exps[["experiment_name", "start_timestamp"]],
social_retreat_df_all_exps[["experiment_name", "start_timestamp"]],
]
)
all_events["start_timestamp"] = pd.to_datetime(all_events["start_timestamp"])
# Merge baseline timestamps
all_events = all_events.merge(
exp_df, left_on="experiment_name", right_on="name", how="left"
)
# Compute seconds since baseline
all_events["rel_sec"] = (
all_events["start_timestamp"] - all_events["baseline_ts"]
).dt.total_seconds()
# Find last event
last = all_events.loc[all_events["rel_sec"].idxmax()]
# Compute end day and hour
end_day = int(last["rel_sec"] // 86400)
end_hour = int((last["rel_sec"] % 86400) // 3600)
print(f"Global end at Day {end_day}, hour {end_hour}")
# Plot each raster
exp_order = [e["name"] for e in experiments]
dark_color = "#555555"
# Dataframes and titles to plot
raster_configs = [
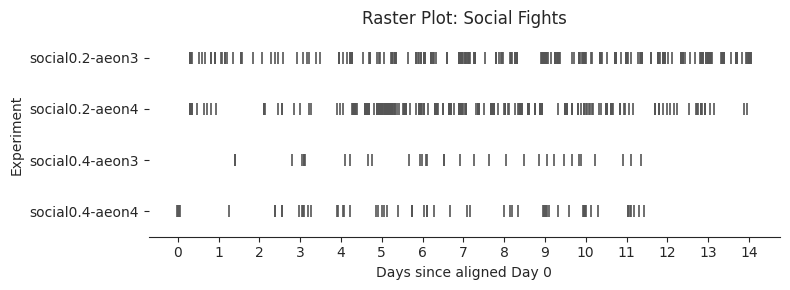
(social_fight_df_all_exps, "Raster Plot: Social Fights", "fights"),
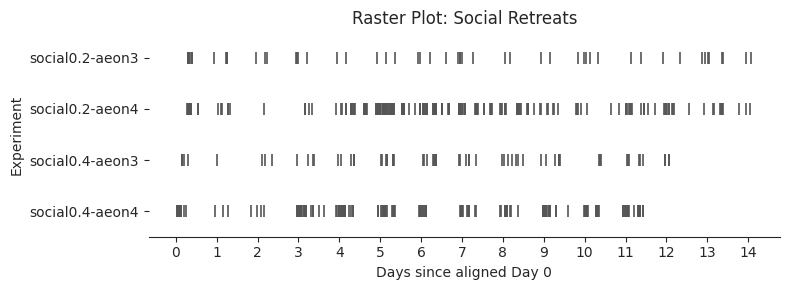
(social_retreat_df_all_exps, "Raster Plot: Social Retreats", "retreats"),
]
for df, title, behavior in raster_configs:
# Convert start_timestamp to datetime in-place
df["start_timestamp"] = pd.to_datetime(df["start_timestamp"])
# Merge with exp_df (overwrite df with merged version)
df = df.merge(exp_df, left_on="experiment_name", right_on="name", how="left")
df = df.drop(columns="name")
# Compute rel_days
df["rel_days"] = (
df["start_timestamp"] - df["baseline_ts"]
).dt.total_seconds() / 86400.0
# Enforce experiment ordering
df["experiment_name"] = pd.Categorical(
df["experiment_name"], categories=exp_order, ordered=True
)
# Create the plots
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 1 + 0.5 * len(exp_order)))
sns.stripplot(
data=df,
x="rel_days",
y="experiment_name",
size=8,
jitter=False,
marker="|",
color=dark_color,
linewidth=1.2,
edgecolor=dark_color,
)
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.MultipleLocator(1))
plt.xlabel("Days since aligned Day 0")
plt.ylabel("Experiment")
plt.title(title)
sns.despine(left=True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Aligned Day 0 starts at hour 10
Global end at Day 14, hour 1
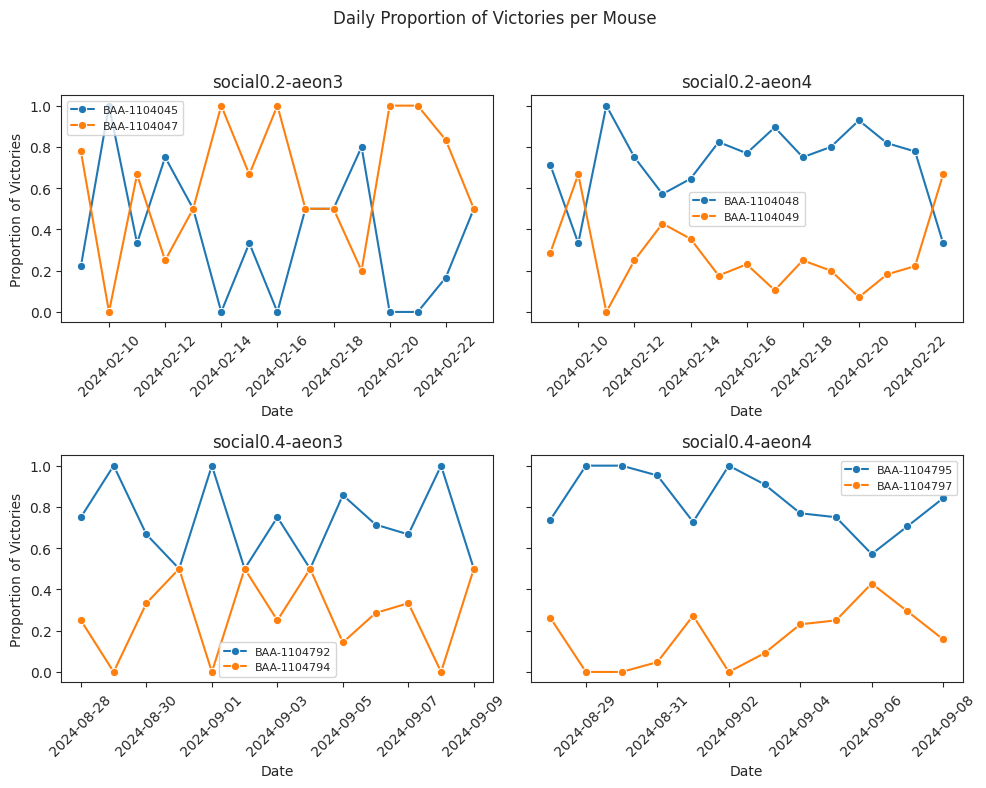
Proportion of retreat event wins over time#
Daily proportion of victories#
# NOT SMOOTHED
# Ensure 'end_timestamp' is datetime and extract 'date'
social_retreat_df_all_exps["end_timestamp"] = pd.to_datetime(
social_retreat_df_all_exps["end_timestamp"]
)
social_retreat_df_all_exps["date"] = social_retreat_df_all_exps["end_timestamp"].dt.date
# Prepare 2×2 grid
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8), sharey=True)
axes = axes.flatten() # Flatten to 1D for easy indexing
# Loop through experiments and plot
for i, (exp_name, df_group) in enumerate(
social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby("experiment_name", observed=True)
):
# Compute daily win-counts per mouse
wins = df_group.groupby(["date", "winner_identity"]).size().unstack(fill_value=0)
# Turn counts into proportions
proportions = wins.div(wins.sum(axis=1), axis=0).reset_index()
# Melt to long form for plotting
df_long = proportions.melt(
id_vars="date", var_name="winner_identity", value_name="proportion"
)
# Plot in grid
ax = axes[i]
sns.lineplot(
data=df_long,
x="date",
y="proportion",
hue="winner_identity",
marker="o",
linewidth=1.5,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_title(f"{exp_name}")
ax.set_xlabel("Date")
ax.tick_params(axis="x", rotation=45)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.DayLocator(interval=2)) # every 2 days
ax.set_ylabel("Proportion of Victories")
# Add legend per subplot
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
by_label = dict(zip(labels, handles))
ax.legend(by_label.values(), by_label.keys(), fontsize=8)
# Clean layout
plt.suptitle("Daily Proportion of Victories per Mouse")
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0, 1, 0.96])
plt.show()
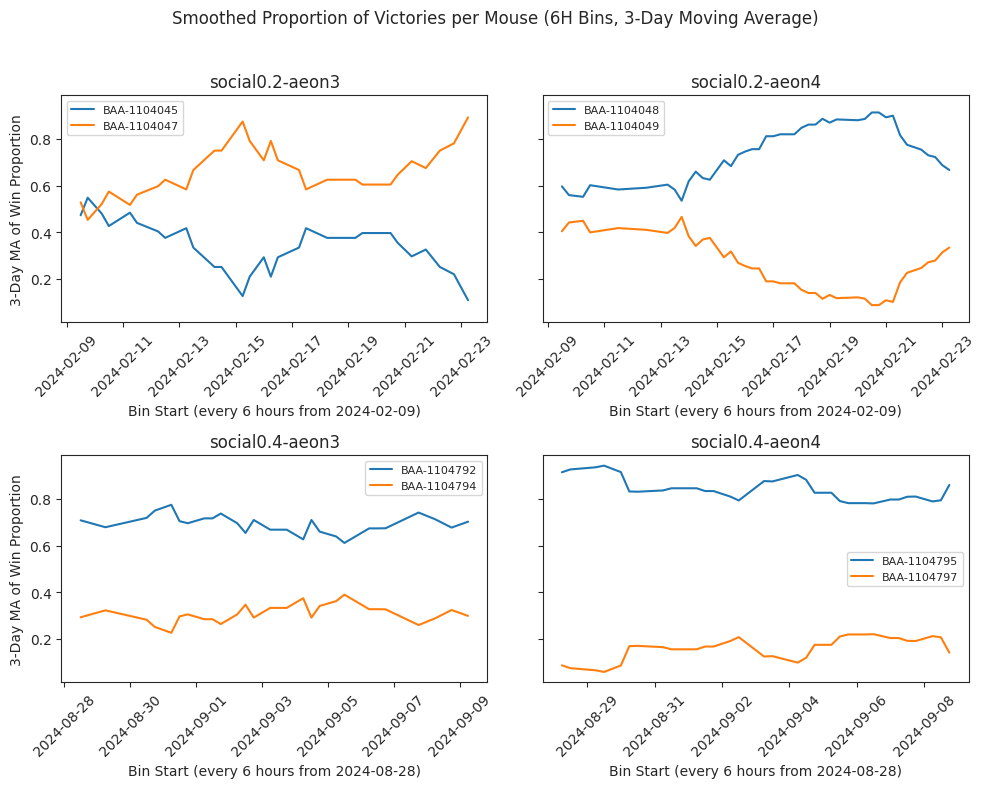
Smoothed proportion of victories#
# SMOOTHED
# Parameters
BIN_HOURS = 6 # how many hours per bin (e.g. 6, 8, 10, 12, etc.)
SMOOTH_DAYS = 3 # how many days to smooth over (e.g. 3, 5, 7, etc.)
# Prepare 2×2 grid
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8), sharey=True)
axes = axes.flatten() # Flatten to 1D for easy indexing
# Loop through experiments and plot
for i, (exp_name, df_group) in enumerate(
social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby("experiment_name", observed=True)
):
# Compute bin start for each timestamp
earliest_midnight = df_group["end_timestamp"].dt.normalize().min()
bin_size = pd.Timedelta(hours=BIN_HOURS)
offsets = df_group["end_timestamp"] - earliest_midnight
n_bins = (offsets // bin_size).astype(int)
df_group["bin_start"] = earliest_midnight + n_bins * bin_size
# Compute win-counts per bin per mouse
wins = (
df_group.groupby(["bin_start", "winner_identity"]).size().unstack(fill_value=0)
)
# Drop bins with zero total wins
wins = wins[wins.sum(axis=1) > 0]
# Turn counts into proportions
proportions = wins.div(wins.sum(axis=1), axis=0).reset_index()
# Melt to long form for plotting
df_long = proportions.melt(
id_vars="bin_start", var_name="winner_identity", value_name="proportion"
)
# Compute moving average window size (in bins)
window_size = int((SMOOTH_DAYS * 24) / BIN_HOURS)
window_size = max(window_size, 1)
# Apply centered moving average per mouse
df_long = df_long.sort_values(["winner_identity", "bin_start"])
df_long["smoothed_prop"] = df_long.groupby("winner_identity")[
"proportion"
].transform(
lambda s: s.rolling(window=window_size, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
)
# Plot in grid
ax = axes[i]
sns.lineplot(
data=df_long,
x="bin_start",
y="smoothed_prop",
hue="winner_identity",
# marker=False,
linewidth=1.5,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_title(f"{exp_name}")
ax.set_xlabel(
f"Bin Start (every {BIN_HOURS} hours from {earliest_midnight.date()})"
)
ax.tick_params(axis="x", rotation=45)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mdates.DayLocator(interval=2)) # every 2 days
ax.set_ylabel(f"{SMOOTH_DAYS}‐Day MA of Win Proportion")
# Add legend per subplot
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
by_label = dict(zip(labels, handles))
ax.legend(by_label.values(), by_label.keys(), fontsize=8)
# Clean layout
plt.suptitle(
f"Smoothed Proportion of Victories per Mouse ({BIN_HOURS}H Bins, {SMOOTH_DAYS}‐Day Moving Average)"
)
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0, 1, 0.96])
plt.show()
# Compute average number of retreat events per experiment-day
social_retreat_df_all_exps["start_timestamp"] = pd.to_datetime(
social_retreat_df_all_exps["start_timestamp"]
)
# Extract day from timestamp
social_retreat_df_all_exps["day"] = social_retreat_df_all_exps[
"start_timestamp"
].dt.floor("D")
# Count events per (experiment, day)
daily_counts = social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby(
["experiment_name", "day"], observed=True
).size()
# Compute global average
avg_events_per_day = daily_counts.mean()
print(f"Average number of retreat events per experiment-day: {avg_events_per_day:.2f}")
Average number of retreat events per experiment-day: 9.89
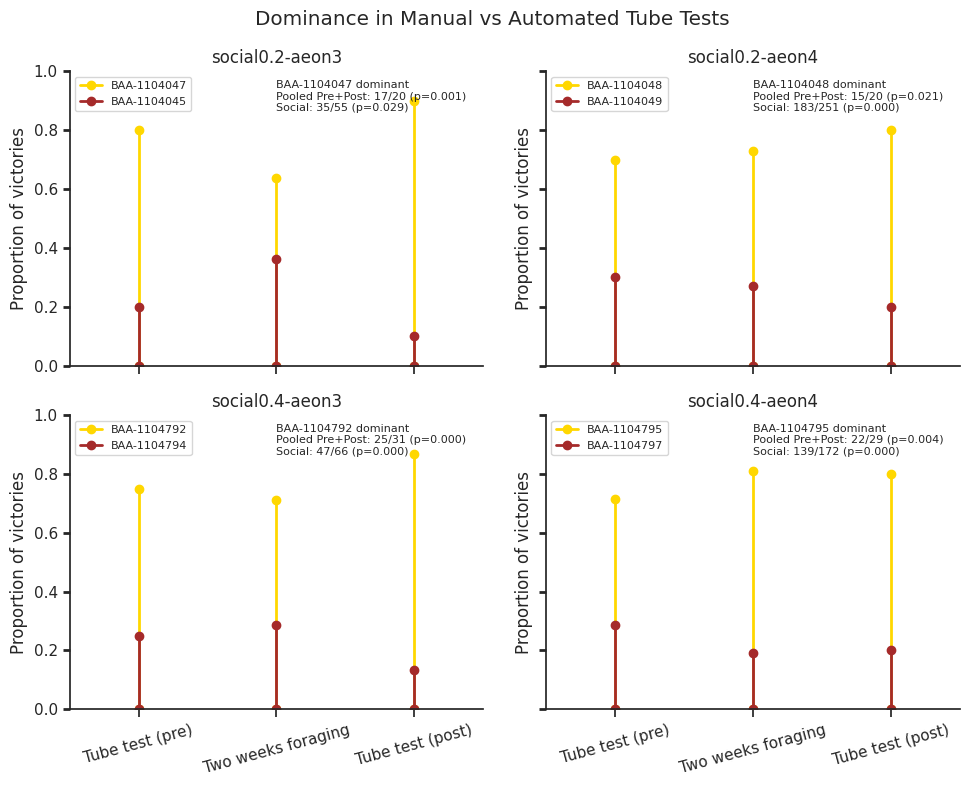
Manual vs. automated tube test#
To validate our automated approach, we also conducted manual tube tests (adapted from Fan et al. 2019) before (“pre-social”) and after (“post-social”) the experiments.
Here we compare manual tube test outcomes with automated dominance rankings derived from retreat behaviours during the experiments, and show that the automated method reliably captures hierarchical relationships over time. Specifically, dominant individuals consistently exhibit a higher proportion of victories, both in manual assays and in automated retreat-based rankings.
Manual tube test outcomes
Group |
Subject ID |
Pre-social |
Post-social |
|---|---|---|---|
social0.2-aeon3 |
BAA-1104045 |
2 |
1 |
BAA-1104047 |
8 |
9 |
|
social0.2-aeon4 |
BAA-1104048 |
7 |
8 |
BAA-1104049 |
3 |
2 |
|
social0.4-aeon3 |
BAA-1104792 |
12 |
13 |
BAA-1104794 |
4 |
2 |
|
social0.4-aeon4 |
BAA-1104795 |
10 |
12 |
BAA-1104797 |
4 |
3 |
# Total win counts per subject during social phase
social_counts_df = (
social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby(["experiment_name", "winner_identity"])
.size()
.unstack(fill_value=0)
)
# Manual tube test data (pre- and post-social)
tube_test_data = {
"social0.2-aeon3": {
"BAA-1104045": {"pre": 2, "post": 1},
"BAA-1104047": {"pre": 8, "post": 9},
},
"social0.2-aeon4": {
"BAA-1104048": {"pre": 7, "post": 8},
"BAA-1104049": {"pre": 3, "post": 2},
},
"social0.4-aeon3": {
"BAA-1104794": {"pre": 4, "post": 2},
"BAA-1104792": {"pre": 12, "post": 13},
},
"social0.4-aeon4": {
"BAA-1104795": {"pre": 10, "post": 12},
"BAA-1104797": {"pre": 4, "post": 3},
},
}
# Compute per-experiment summary metrics for dominant subject
records = []
for exp, subj_dict in tube_test_data.items():
soc_counts = social_counts_df.loc[exp]
total_pre = sum(d["pre"] for d in subj_dict.values())
total_post = sum(d["post"] for d in subj_dict.values())
total_soc = soc_counts.sum()
# Identify dominant by total wins across all phases
total_wins = {
subj: subj_dict[subj]["pre"] + soc_counts.get(subj, 0) + subj_dict[subj]["post"]
for subj in subj_dict
}
dominant = max(total_wins, key=total_wins.get)
# Compute win rates for dominant subject
pre_rate = subj_dict[dominant]["pre"] / total_pre
social_rate = soc_counts[dominant] / total_soc
post_rate = subj_dict[dominant]["post"] / total_post
baseline_rate = (subj_dict[dominant]["pre"] + subj_dict[dominant]["post"]) / (
total_pre + total_post
)
records.append(
{
"experiment": exp,
"dominant": dominant,
"pre_rate": pre_rate,
"social_rate": social_rate,
"post_rate": post_rate,
"baseline_rate": baseline_rate,
}
)
summary_df = pd.DataFrame(records)
# Test: is social-phase rate higher than pre+post (Wilcoxon signed-rank)
stat, p_value = wilcoxon(summary_df["baseline_rate"], summary_df["social_rate"])
print(f"Wilcoxon signed-rank: W = {stat:.3f}, p-value = {p_value:.3f}\n")
# Per-experiment plotting and binomial tests
x_positions = [0, 1, 2]
x_labels = ["Tube test (pre)", "Two weeks foraging", "Tube test (post)"]
phase_order = ["pre", "social", "post"]
plot_data = []
annotations = []
for experiment, subjects in tube_test_data.items():
ids = list(subjects.keys())
pre_scores = {s: subjects[s]["pre"] for s in ids}
post_scores = {s: subjects[s]["post"] for s in ids}
soc_counts = social_counts_df.loc[experiment]
dominant = summary_df.loc[summary_df["experiment"] == experiment, "dominant"].iloc[
0
]
subordinate = [s for s in ids if s != dominant][0]
# Win/loss counts
k_pre = pre_scores[dominant]
n_pre = k_pre + pre_scores[subordinate]
k_post = post_scores[dominant]
n_post = k_post + post_scores[subordinate]
k_social = soc_counts[dominant]
n_social = soc_counts.sum()
# Binomial tests
k_pool = k_pre + k_post
n_pool = n_pre + n_post
p_pool = binomtest(k_pool, n_pool, p=0.5, alternative="greater").pvalue
p_social = binomtest(k_social, n_social, p=0.5, alternative="greater").pvalue
# Annotation text
annotation = (
f"{dominant} dominant\n"
f"Pooled Pre+Post: {k_pool}/{n_pool} (p={p_pool:.3f})\n"
f"Social: {k_social}/{n_social} (p={p_social:.3f})"
)
annotations.append((experiment, annotation))
# Proportions
proportions = {
dominant: {
"pre": k_pre / n_pre,
"social": k_social / n_social,
"post": k_post / n_post,
"color": "gold",
},
subordinate: {
"pre": pre_scores[subordinate] / n_pre,
"social": soc_counts[subordinate] / n_social,
"post": post_scores[subordinate] / n_post,
"color": "brown",
},
}
for subj, vals in proportions.items():
for phase, x in zip(phase_order, x_positions):
plot_data.append(
{
"Experiment": experiment,
"Subject": subj,
"Phase": phase,
"X": x,
"Y": vals[phase],
"Color": vals["color"],
}
)
df = pd.DataFrame(plot_data)
# Plotting in 2x2 grid
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8), sharex=True, sharey=True)
axes = axes.flatten()
for i, experiment in enumerate([exp["name"] for exp in experiments]):
ax = axes[i]
subset = df[df["Experiment"] == experiment]
# Draw vertical lines with markers
for subj in subset["Subject"].unique():
subj_data = subset[subset["Subject"] == subj]
for _, row in subj_data.iterrows():
ax.plot(
[row["X"], row["X"]],
[0, row["Y"]],
color=row["Color"],
marker="o",
label=subj if row["Phase"] == "pre" else "",
linewidth=2,
)
ax.set_title(experiment)
ax.set_xticks(x_positions)
ax.set_xticklabels(x_labels, rotation=15)
ax.set_xlim(-0.5, 2.5)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylabel("Proportion of victories")
ax.spines["top"].set_visible(False)
ax.spines["right"].set_visible(False)
ax.tick_params(axis="y", direction="out", length=5, width=2)
# Add annotation
_, annotation = annotations[i]
ax.text(
0.5,
0.97,
annotation,
transform=ax.transAxes,
fontsize=8,
verticalalignment="top",
)
# Add legend per subplot
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
by_label = dict(zip(labels, handles))
ax.legend(by_label.values(), by_label.keys(), fontsize=8, loc="upper left")
plt.suptitle("Dominance in Manual vs Automated Tube Tests")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Wilcoxon signed-rank: W = 2.000, p-value = 0.375
Dominance summary plot#
social_win_proportions = (
social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby(["experiment_name", "winner_identity"])
.size()
.unstack(fill_value=0)
)
social_win_proportions = social_win_proportions.div(
social_win_proportions.sum(axis=1), axis=0
)
# Prepare long-form data
plot_rows = []
for experiment, subjects in tube_test_data.items():
ids = list(subjects.keys())
pre_scores = {subj: subjects[subj]["pre"] for subj in ids}
post_scores = {subj: subjects[subj]["post"] for subj in ids}
pre_dominant = max(pre_scores, key=pre_scores.get)
post_dominant = max(post_scores, key=post_scores.get)
if experiment not in social_win_proportions.index:
raise ValueError(f"No social data for {experiment}")
social_scores = social_win_proportions.loc[experiment]
social_dominant = social_scores.idxmax()
if len({pre_dominant, post_dominant, social_dominant}) != 1:
raise ValueError(
f"Inconsistent dominant subject in {experiment}: pre={pre_dominant}, social={social_dominant}, post={post_dominant}"
)
dominant = pre_dominant
subordinate = [s for s in ids if s != dominant][0]
total_pre = pre_scores[dominant] + pre_scores[subordinate]
total_post = post_scores[dominant] + post_scores[subordinate]
social_dom = (
social_win_proportions.at[experiment, dominant]
if dominant in social_win_proportions.columns
else 0
)
social_sub = (
social_win_proportions.at[experiment, subordinate]
if subordinate in social_win_proportions.columns
else 0
)
for role, subj, color in [
("Dominant", dominant, "gold"),
("Subordinate", subordinate, "brown"),
]:
plot_rows.append(
{
"experiment": experiment,
"subject": subj,
"role": role,
"color": color,
"x_pre": -pre_scores[subj] / total_pre,
"x_post": post_scores[subj] / total_post,
"y_social": -social_win_proportions.at[experiment, subj],
}
)
df = pd.DataFrame(plot_rows)
# Create mirrored points for post phase
df_post = df.copy()
df_post["x"] = df_post["x_post"]
df_post["y"] = -df_post["y_social"]
df_pre = df.copy()
df_pre["x"] = df_pre["x_pre"]
df_pre["y"] = df_pre["y_social"]
df_all = pd.concat([df_pre, df_post], ignore_index=True)
# Plot
sns.set(style="ticks")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 6))
sns.scatterplot(
data=df_all,
x="x",
y="y",
hue="role",
palette={"Dominant": "gold", "Subordinate": "brown"},
s=50,
ax=ax,
)
# Draw quadrant axes
ax.axhline(0, color="black", linewidth=1)
ax.axvline(0, color="black", linewidth=1)
# Draw ticks at ±1
tick_len = 0.02
for t in [-1, 1]:
ax.plot([t, t], [-tick_len, tick_len], color="black", linewidth=1) # x-axis ticks
ax.plot([-tick_len, tick_len], [t, t], color="black", linewidth=1) # y-axis ticks
# Annotate ±1 labels
ax.text(-1, -0.08, "−1", ha="center", va="top", fontsize=12)
ax.text(1, -0.08, "1", ha="center", va="top", fontsize=12)
ax.text(0.08, -1, "−1", ha="left", va="center", fontsize=12)
ax.text(0.08, 1, "1", ha="left", va="center", fontsize=12)
# Diagonal reference line
ax.plot([-1, 1], [-1, 1], linestyle="--", color="lightgrey", linewidth=1)
# Axis styling
ax.set_xlim(-1.1, 1.1)
ax.set_ylim(-1.1, 1.1)
ax.set_xlabel("Tube test victory proportion (−pre, +post)")
ax.set_ylabel("Social phase proportion (−pre, +post)")
ax.set_title("Pre vs Post Tube Test (Reflected by Social Proportion)")
sns.despine(ax=ax, left=True, bottom=True)
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
plt.legend(title="Subject role")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
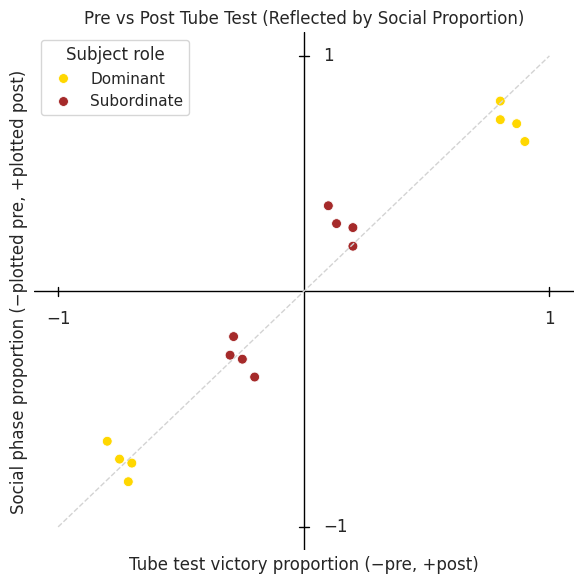
Dominant vs. subordinate at “rich” patch#
df = social_patch_df_all_exps.merge(
social_patchinfo_df_all_exps[
["experiment_name", "block_start", "patch_name", "patch_rate"]
],
on=["experiment_name", "block_start", "patch_name"],
how="left",
).assign(dummy=lambda x: x["patch_name"].str.contains("dummy", case=False))
# Keep only blocks where non-dummy patches have exactly 3 different rates
df = df[
df.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start"])["patch_rate"].transform(
lambda s: s[~df.loc[s.index, "dummy"]].nunique() == 3
)
]
# Create a ranking only for non-dummy patches
non_dummy_ranks = (
df[~df["dummy"]]
.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start"])["patch_rate"]
.rank(method="dense")
)
# Add the ranks back to the full dataframe
df["patch_rank"] = np.nan
df.loc[~df["dummy"], "patch_rank"] = non_dummy_ranks
# Assign difficulty (rank 1=hard, rank 3=easy, rank 2=medium)
df["patch_difficulty"] = np.where(
df["dummy"],
"dummy",
np.where(
df["patch_rank"] == 1, "hard", np.where(df["patch_rank"] == 3, "easy", "medium")
),
)
df = df.drop(columns=["patch_rank"])
# Compute social‐win proportions
swp = (
social_retreat_df_all_exps.groupby(["experiment_name", "winner_identity"])
.size()
.unstack(fill_value=0)
)
swp = swp.div(swp.sum(axis=1), axis=0)
# Build the dominance DataFrame in one comprehension
dominance_df = pd.DataFrame(
[
{
"experiment_name": exp,
"dominant": dom,
"subordinate": next(s for s in subs if s != dom),
}
for exp, subs in tube_test_data.items()
if exp in swp.index
# pick the pre‐tube top scorer…
for dom in [max(subs, key=lambda s: subs[s]["pre"])]
# …only keep if post‐tube and social‐win agree
if dom == max(subs, key=lambda s: subs[s]["post"]) == swp.loc[exp].idxmax()
]
)
dominance_df
| experiment_name | dominant | subordinate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | social0.2-aeon3 | BAA-1104047 | BAA-1104045 |
| 1 | social0.2-aeon4 | BAA-1104048 | BAA-1104049 |
| 2 | social0.4-aeon3 | BAA-1104792 | BAA-1104794 |
| 3 | social0.4-aeon4 | BAA-1104795 | BAA-1104797 |
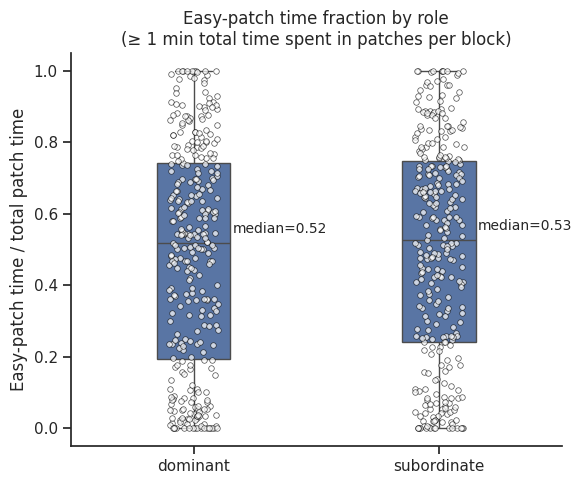
Relative time in easy patch#
# Compute per‐subject, per‐block easy‐time fraction, but only keep blocks ≥1 min
time_df = (
df.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start", "subject_name", "patch_difficulty"])[
"in_patch_time"
]
.sum()
.unstack("patch_difficulty", fill_value=0)
.assign(total_time=lambda d: d.sum(axis=1))
# filter out blocks with < 60 s total patch time
.loc[lambda d: d["total_time"] >= 60]
.assign(easy_ratio=lambda d: d["easy"] / d["total_time"])
.reset_index()
)
# Merge in dominant/subordinate labels and tag role
time_df = time_df.merge(dominance_df, on="experiment_name", how="left").assign(
role=lambda d: np.where(
d["subject_name"] == d["dominant"], "dominant", "subordinate"
)
)
# Box‐plot of easy_ratio by role
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 5))
# Draw boxplot with all points
sns.boxplot(
data=time_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
ax=ax,
width=0.3,
)
sns.stripplot(
data=time_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
size=4,
ax=ax,
marker="o",
edgecolor="black",
linewidth=0.5,
facecolor="white",
alpha=0.7,
)
sns.despine(ax=ax)
# Axis labels and title
ax.set_title(
"Easy-patch time fraction by role\n(≥ 1 min total time spent in patches per block)"
)
ax.set_ylabel("Easy-patch time / total patch time")
ax.set_xlabel("")
# Calculate medians
medians = time_df.groupby("role")["easy_ratio"].median()
# Add annotations
for i, role in enumerate(["dominant", "subordinate"]):
median_val = medians[role]
ax.text(
i + 0.35,
median_val + 0.02,
f"median={median_val:.2f}",
ha="center",
va="bottom",
fontsize=10,
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Get per‐subject, per‐block time by difficulty
time_df = (
df.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start", "subject_name", "patch_difficulty"])[
"in_patch_time"
]
.sum()
.unstack("patch_difficulty", fill_value=0)
# drop any block‐subject that didn’t spend ≥10 s in each of hard/medium/easy
.loc[lambda d: (d[["hard", "medium", "easy"]] >= 10).all(axis=1)]
.assign(
total_time=lambda d: d.sum(axis=1),
easy_ratio=lambda d: d["easy"] / d["total_time"],
)
.reset_index()
)
# Merge in dominant/subordinate and label role
time_df = time_df.merge(dominance_df, on="experiment_name", how="left").assign(
role=lambda d: np.where(
d["subject_name"] == d["dominant"], "dominant", "subordinate"
)
)
# Box‐plot of easy_ratio by role
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 5))
# Draw boxplot with all points
sns.boxplot(
data=time_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
ax=ax,
width=0.3,
)
sns.stripplot(
data=time_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
size=4,
ax=ax,
marker="o",
edgecolor="black",
linewidth=0.5,
facecolor="white",
alpha=0.7,
)
sns.despine(ax=ax)
# Axis labels and title
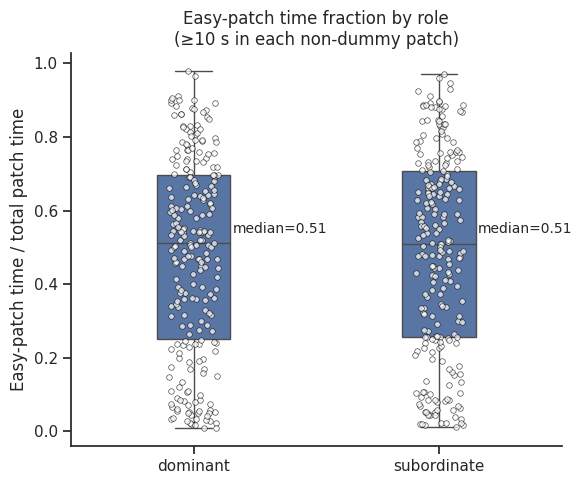
ax.set_title("Easy-patch time fraction by role\n(≥10 s in each non-dummy patch)")
ax.set_ylabel("Easy-patch time / total patch time")
ax.set_xlabel("")
# Calculate medians
medians = time_df.groupby("role")["easy_ratio"].median()
# Add annotations
for i, role in enumerate(["dominant", "subordinate"]):
median_val = medians[role]
ax.text(
i + 0.35,
median_val + 0.02,
f"median={median_val:.2f}",
ha="center",
va="bottom",
fontsize=10,
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Relative wheel distance spun in easy patch#
# Compute true traveled distance for each patch‐visit, thresholding <1→0
df2 = (
df.assign(
# sum of abs steps = true distance
traveled=lambda d: d["wheel_cumsum_distance_travelled"].apply(
lambda arr: np.sum(np.abs(np.diff(arr))) if len(arr) > 1 else 0
)
)
# any tiny (<1) distance becomes 0
.assign(traveled=lambda d: d["traveled"].mask(d["traveled"] < 1, 0))
)
# Pivot to one row per subject‐block with columns [hard, medium, easy]
dist_df = (
df2.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start", "subject_name", "patch_difficulty"])[
"traveled"
]
.sum()
.unstack("patch_difficulty", fill_value=0)
.assign(
total_dist=lambda d: d.sum(axis=1),
easy_ratio=lambda d: d["easy"] / d["total_dist"],
)
.reset_index()
)
# Merge in dominance & tag role
dist_df = dist_df.merge(dominance_df, on="experiment_name", how="left").assign(
role=lambda d: np.where(
d["subject_name"] == d["dominant"], "dominant", "subordinate"
)
)
# Box‐plot of easy_ratio by role
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 5))
# Draw boxplot with all points
sns.boxplot(
data=dist_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
ax=ax,
width=0.3,
)
sns.stripplot(
data=dist_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
size=4,
ax=ax,
marker="o",
edgecolor="black",
linewidth=0.5,
facecolor="white",
alpha=0.7,
)
sns.despine(ax=ax)
# Axis labels and title
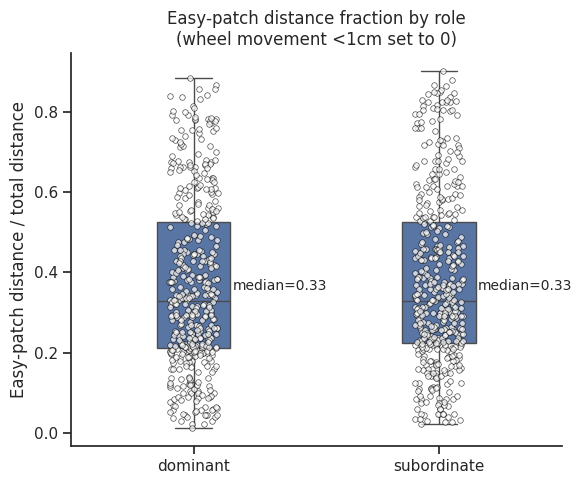
ax.set_title("Easy‐patch distance fraction by role\n(wheel movement <1cm set to 0)")
ax.set_ylabel("Easy‐patch distance / total distance")
ax.set_xlabel("")
# Calculate medians
medians = dist_df.groupby("role")["easy_ratio"].median()
# Add annotations
for i, role in enumerate(["dominant", "subordinate"]):
median_val = medians[role]
ax.text(
i + 0.35,
median_val + 0.02,
f"median={median_val:.2f}",
ha="center",
va="bottom",
fontsize=10,
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Compute true traveled distance per patch‐visit, tiny spins → 0
df2 = df.assign(
traveled=lambda d: d["wheel_cumsum_distance_travelled"].apply(
lambda arr: np.sum(np.abs(np.diff(arr))) if len(arr) > 1 else 0
)
).assign(traveled=lambda d: d["traveled"].mask(d["traveled"] < 1, 0))
# Pivot to one row per subject‐block, but only keep rows where hard,medium,easy >5
dist_df = (
df2.groupby(["experiment_name", "block_start", "subject_name", "patch_difficulty"])[
"traveled"
]
.sum()
.unstack("patch_difficulty", fill_value=0)
.loc[lambda d: (d[["hard", "medium", "easy"]] > 500).all(axis=1)]
.assign(
total_dist=lambda d: d.sum(axis=1),
easy_ratio=lambda d: d["easy"] / d["total_dist"],
)
.reset_index()
)
# Merge in dominance & tag role
dist_df = dist_df.merge(dominance_df, on="experiment_name", how="left").assign(
role=lambda d: np.where(
d["subject_name"] == d["dominant"], "dominant", "subordinate"
)
)
# Box‐plot of easy_ratio by role
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 5))
# Draw boxplot with all points
sns.boxplot(
data=dist_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
ax=ax,
width=0.3,
)
sns.stripplot(
data=dist_df,
x="role",
y="easy_ratio",
order=["dominant", "subordinate"],
size=4,
ax=ax,
marker="o",
edgecolor="black",
linewidth=0.5,
facecolor="white",
alpha=0.7,
)
sns.despine(ax=ax)
# Axis labels and title
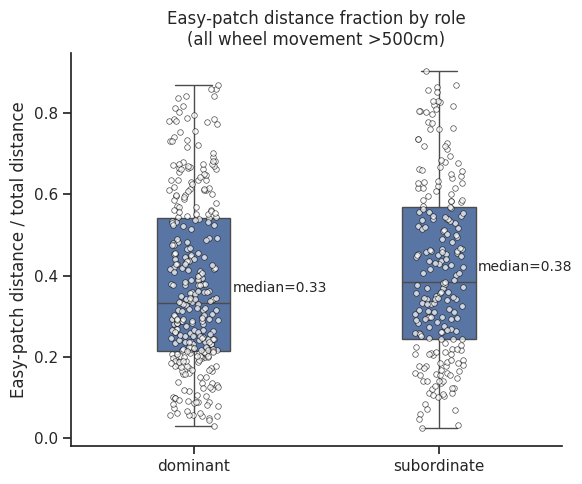
ax.set_title("Easy-patch distance fraction by role\n(all wheel movement >500cm)")
ax.set_ylabel("Easy-patch distance / total distance")
ax.set_xlabel("")
# Calculate medians
medians = dist_df.groupby("role")["easy_ratio"].median()
# Add annotations
for i, role in enumerate(["dominant", "subordinate"]):
median_val = medians[role]
ax.text(
i + 0.35,
median_val + 0.02,
f"median={median_val:.2f}",
ha="center",
va="bottom",
fontsize=10,
)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
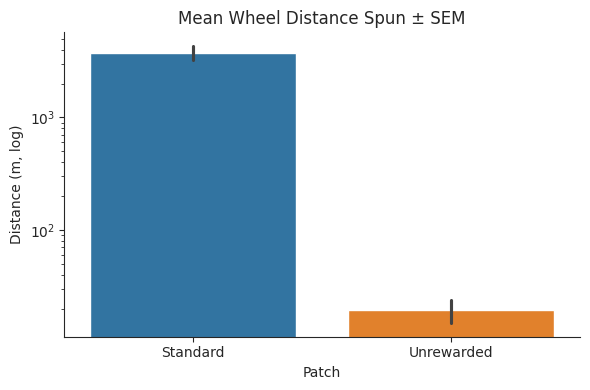
Unrewarded vs. standard patches#
In the social0.4 experiments, a fourth “unrewarded” patch on which the pellet dispenser unit was inactive was introduced as a control.
We compare the foraging wheel activity across patch types and show that subjects spun the wheel significantly more on standard patches where the pellet dispenser unit was active.
Load data#
patch_dfs = []
for exp in [exp for exp in experiments if exp["name"].startswith("social0.4")]:
data = load_experiment_data(experiment=exp, data_dir=data_dir, data_types=["patch"])
df = data["None_patch"]
patch_dfs.append(df)
patch_df_s4 = pd.concat(patch_dfs).sort_index()
dt_seconds = 0.02 # Wheel sampling interval in seconds
summary = []
# Compute total distance spun per (subject, patch)
for (subject, patch), grp in patch_df_s4.groupby(["subject_name", "patch_name"]):
total_distance = sum(
np.asarray(w)[-1] for w in grp["wheel_cumsum_distance_travelled"] if len(w) > 0
)
summary.append(
{"subject": subject, "patch": patch, "distance": total_distance / 100}
) # convert to meters
summary_df = pd.DataFrame(summary)
summary_df["patch_type"] = summary_df["patch"].apply(
lambda p: "Unrewarded" if "Dummy" in p else "Standard"
)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
sns.barplot(
data=summary_df,
x="patch_type",
y="distance",
hue="patch_type",
errorbar="se",
)
plt.yscale("log")
plt.ylabel("Distance (m, log)")
plt.xlabel("Patch")
plt.title("Mean Wheel Distance Spun ± SEM")
sns.despine()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
summary_patch_type_df = (
summary_df.groupby(["subject", "patch_type"])["distance"].mean().unstack()
)
t_stat, p_val = ttest_rel(
summary_patch_type_df["Unrewarded"], summary_patch_type_df["Standard"]
)
print(f"Paired t‐statistic = {t_stat:.3f}, p‐value = {p_val:.4f}")
summary_patch_type_df
Paired t‐statistic = -17.706, p‐value = 0.0004
| patch_type | Standard | Unrewarded |
|---|---|---|
| subject | ||
| BAA-1104792 | 4300.985857 | 25.288925 |
| BAA-1104794 | 3847.328388 | 20.960074 |
| BAA-1104795 | 3551.048284 | 24.882764 |
| BAA-1104797 | 3306.791160 | 6.401984 |
Weight#
Load data#
social_weight_dfs = []
for exp in experiments:
data = load_experiment_data(
experiment=exp, data_dir=data_dir, periods=["social"], data_types=["weight"]
)
df = data["social_weight"]
social_weight_dfs.append(df)
social_weight_df_all_exps = pd.concat(social_weight_dfs).sort_index()
Averaged over time per subject#
# Flatten the “array-of-arrays” df into a long DataFrame
records = []
for _, row in social_weight_df_all_exps.iterrows():
ts = pd.to_datetime(row["timestamps"])
w = np.asarray(row["weight"], dtype=float)
sids = row["subject_id"]
for t, weight, sid in zip(ts, w, sids):
records.append({"timestamp": t, "subject_id": sid, "weight": weight})
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(records)
df = df.sort_values(["subject_id", "timestamp"])
# Drop rows where subject_id is shorter than 11 characters, removes some erroneous entries
df = df[df["subject_id"].str.len() >= 11].reset_index(drop=True)
# Parameters & 24 h cycle grid
sampling_freq = "10min" # resample interval
# Choose any date at 08:00 to define “day zero”
anchor = pd.Timestamp(f"2020-01-01 {light_off:02d}:00:00")
# Build the 24 h cycle index
n_steps = int(pd.Timedelta("1D") / pd.Timedelta(sampling_freq))
cycle_index = pd.timedelta_range(start=0, periods=n_steps, freq=sampling_freq)
# Will hold each mouse’s mean‐day
cycle_df = pd.DataFrame(index=cycle_index)
# Loop over each mouse, resample, fold into 24 h, average days
for sid, grp in df.groupby("subject_id"):
# Series of weight vs time
ser = grp.set_index("timestamp")["weight"].sort_index()
# Collapse any exact-duplicate timestamps
ser = ser.groupby(level=0).mean()
# Resample into bins anchored at 08:00, then interpolate
ser_rs = ser.resample(sampling_freq, origin=anchor).mean().interpolate()
# Convert each timestamp into its offset (mod 24 h) from the anchor
offsets = (ser_rs.index - anchor) % pd.Timedelta("1D")
ser_rs.index = offsets
# Average across all days for each offset
daily = ser_rs.groupby(ser_rs.index).mean()
# Align to uniform cycle grid
cycle_df[sid] = daily.reindex(cycle_index)
# Baseline‐subtract each mouse’s minimum, then grand‐mean
cycle_df_baselined = cycle_df.subtract(cycle_df.min(skipna=True), axis=1)
grand_mean = cycle_df_baselined.mean(axis=1)
sem = cycle_df_baselined.sem(axis=1)
# Smooth both mean and SEM with a centered rolling window
window = 20
grand_mean_smooth = grand_mean.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
sem_smooth = sem.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
# Plot each subject's mean-day curve in its own subplot
n_subj = cycle_df_baselined.shape[1]
n_cols = 4 # adjust as needed
n_rows = math.ceil(n_subj / n_cols)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(
n_rows, n_cols, figsize=(3.5 * n_cols, 2.5 * n_rows), sharex=True, sharey=True
)
axes = axes.flatten()
x_hours = cycle_df_baselined.index.total_seconds() / 3600
for i, sid in enumerate(cycle_df_baselined.columns):
ax = axes[i]
y = cycle_df_baselined[sid]
y_smooth = y.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
ax.plot(x_hours, y_smooth, lw=1.5)
ax.set_title(sid, fontsize=9)
ax.set_xlim(0, 24)
ax.grid(True, linestyle=":", linewidth=0.5)
# Remove any unused axes
for ax in axes[n_subj:]:
ax.set_visible(False)
fig.suptitle("24h weight cycle (baseline-subtracted) per subject", y=1.02)
fig.text(0.5, 0.04, f"Time since {light_off:02d}:00:00 (hours)", ha="center")
fig.text(0.04, 0.5, "Weight (baseline-subtracted)", va="center", rotation="vertical")
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.4, wspace=0.3, bottom=0.1, left=0.07, right=0.97, top=0.90)
plt.show()
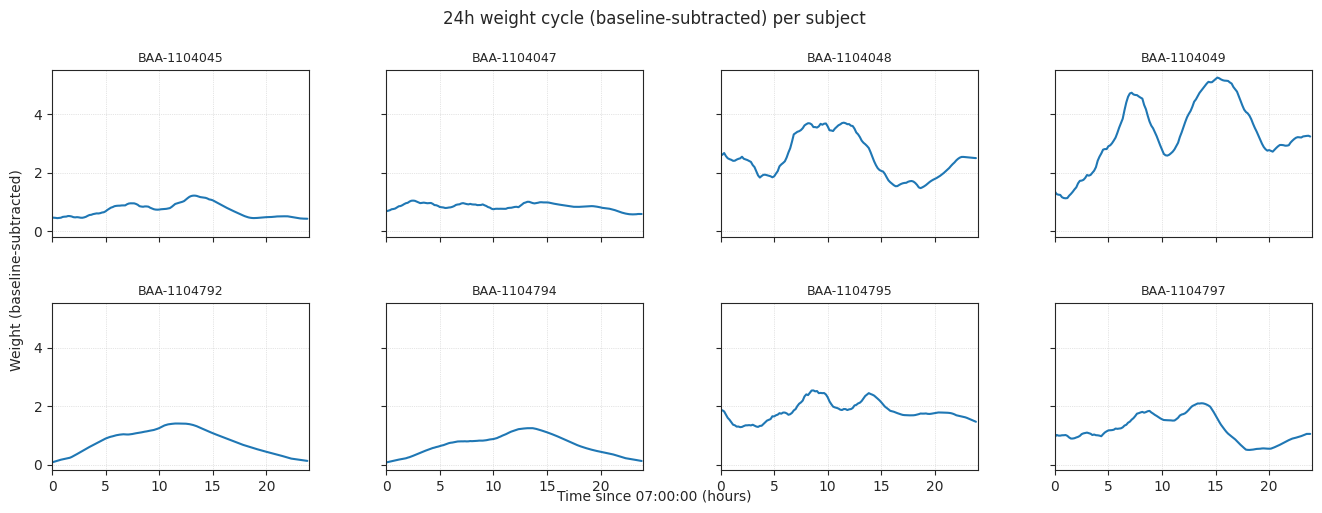
Averaged over time and subjects#
Baselined by subtracting the minimum of each subject’s 24h mean-day curve
# Flatten the “array-of-arrays” df into a long DataFrame
records = []
for _, row in social_weight_df_all_exps.iterrows():
ts = pd.to_datetime(row["timestamps"])
w = np.asarray(row["weight"], dtype=float)
sids = row["subject_id"]
for t, weight, sid in zip(ts, w, sids):
records.append({"timestamp": t, "subject_id": sid, "weight": weight})
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(records)
df = df.sort_values(["subject_id", "timestamp"])
# Drop rows where subject_id is shorter than 11 characters, removes some erroneous entries
df = df[df["subject_id"].str.len() >= 11].reset_index(drop=True)
# Parameters & 24 h cycle grid
sampling_freq = "10min" # resample interval
# Choose any date at 08:00 to define “day zero”
anchor = pd.Timestamp(f"2020-01-01 {light_off:02d}:00:00")
# Build the 24 h cycle index
n_steps = int(pd.Timedelta("1D") / pd.Timedelta(sampling_freq))
cycle_index = pd.timedelta_range(start=0, periods=n_steps, freq=sampling_freq)
# Will hold each mouse’s mean‐day
cycle_df = pd.DataFrame(index=cycle_index)
# Loop over each mouse, resample, fold into 24 h, average days
for sid, grp in df.groupby("subject_id"):
# Series of weight vs time
ser = grp.set_index("timestamp")["weight"].sort_index()
# Collapse any exact-duplicate timestamps
ser = ser.groupby(level=0).mean()
# Resample into bins anchored at 08:00, then interpolate
ser_rs = ser.resample(sampling_freq, origin=anchor).mean().interpolate()
# Convert each timestamp into its offset (mod 24 h) from the anchor
offsets = (ser_rs.index - anchor) % pd.Timedelta("1D")
ser_rs.index = offsets
# Average across all days for each offset
daily = ser_rs.groupby(ser_rs.index).mean()
# Align to uniform cycle grid
cycle_df[sid] = daily.reindex(cycle_index)
# Baseline‐subtract each mouse’s minimum, then grand‐mean
cycle_df_baselined = cycle_df.subtract(cycle_df.min())
grand_mean = cycle_df_baselined.mean(axis=1)
sem = cycle_df_baselined.sem(axis=1)
# Smooth both mean and SEM with a centered rolling window
window = 20
grand_mean_smooth = grand_mean.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
sem_smooth = sem.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
# Plot mean ± SEM
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
x_hours = cycle_df_baselined.index.total_seconds() / 3600
plt.plot(x_hours, grand_mean_smooth, lw=2, label="Mean weight")
plt.fill_between(
x_hours,
grand_mean_smooth - sem_smooth,
grand_mean_smooth + sem_smooth,
alpha=0.3,
label="± SEM",
)
plt.xlabel(f"Time since {light_off:02d}:00:00 (hours)")
plt.ylabel("Weight (baseline-subtracted)")
plt.title("Average 24h weight cycle across all mice\n(Mean ± SEM)")
plt.xlim(0, 24)
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
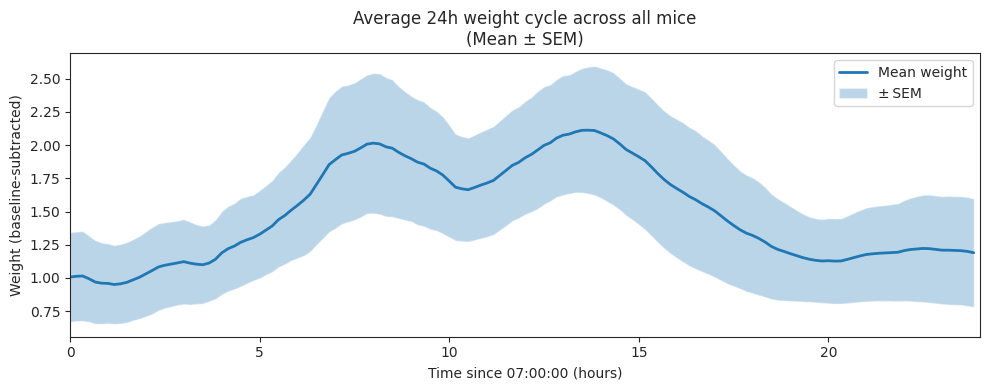
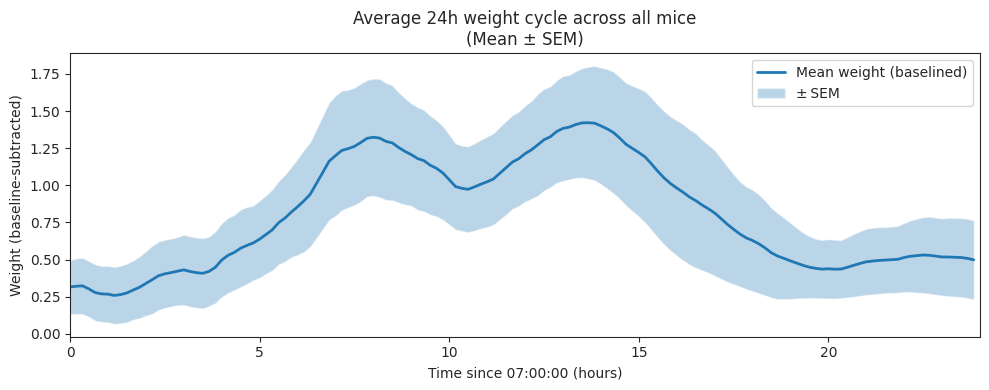
Baselined by subtracting the minimum of each subject’s smoothed 24h mean-day curve
# Flatten the “array-of-arrays” df into a long DataFrame
records = []
for _, row in social_weight_df_all_exps.iterrows():
ts = pd.to_datetime(row["timestamps"])
w = np.asarray(row["weight"], dtype=float)
sids = row["subject_id"]
for t, weight, sid in zip(ts, w, sids):
records.append({"timestamp": t, "subject_id": sid, "weight": weight})
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(records)
df = df.sort_values(["subject_id", "timestamp"])
# Drop rows where subject_id is shorter than 11 characters, removes some erroneous entries
df = df[df["subject_id"].str.len() >= 11].reset_index(drop=True)
# Parameters & 24 h cycle grid
sampling_freq = "10min" # resample interval
# Choose any date at 08:00 to define “day zero”
anchor = pd.Timestamp(f"2020-01-01 {light_off:02d}:00:00")
# Build the 24 h cycle index
n_steps = int(pd.Timedelta("1D") / pd.Timedelta(sampling_freq))
cycle_index = pd.timedelta_range(start=0, periods=n_steps, freq=sampling_freq)
# Will hold each mouse’s mean‐day (unsmoothed)
cycle_df = pd.DataFrame(index=cycle_index)
# Loop over each mouse, resample, fold into 24 h, average days
for sid, grp in df.groupby("subject_id"):
# Series of weight vs time
ser = grp.set_index("timestamp")["weight"].sort_index()
# Collapse any exact-duplicate timestamps
ser = ser.groupby(level=0).mean()
# Resample into bins anchored at 08:00, then interpolate
ser_rs = ser.resample(sampling_freq, origin=anchor).mean().interpolate()
# Convert each timestamp into its offset (mod 24 h) from the anchor
offsets = (ser_rs.index - anchor) % pd.Timedelta("1D")
ser_rs.index = offsets
# Average across all days for each offset
daily = ser_rs.groupby(ser_rs.index).mean()
# Align to uniform cycle grid
cycle_df[sid] = daily.reindex(cycle_index)
# Baseline‐subtract using each subject’s smoothed minimum
window = 20 # keep same smoothing window for per‐subject curves
# Smooth each column (i.e., each subject’s 24 h curve)
cycle_df_smooth = cycle_df.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
# Find the minimum of each subject’s smoothed curve
minima_smooth = cycle_df_smooth.min() # series indexed by subject_id
# Subtract that baseline from the UNSMOOTHED cycle for each subject
cycle_df_baselined = cycle_df.subtract(minima_smooth, axis=1)
# Now compute grand‐mean and SEM (over baselined, unsmoothed curves)
grand_mean = cycle_df_baselined.mean(axis=1)
sem = cycle_df_baselined.sem(axis=1)
# Smooth both grand‐mean and SEM for plotting
grand_mean_smooth = grand_mean.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
sem_smooth = sem.rolling(window=window, center=True, min_periods=1).mean()
# Plot mean ± SEM
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
x_hours = cycle_df_baselined.index.total_seconds() / 3600
plt.plot(x_hours, grand_mean_smooth, lw=2, label="Mean weight (baselined)")
plt.fill_between(
x_hours,
grand_mean_smooth - sem_smooth,
grand_mean_smooth + sem_smooth,
alpha=0.3,
label="± SEM",
)
plt.xlabel(f"Time since {light_off:02d}:00:00 (hours)")
plt.ylabel("Weight (baseline‐subtracted)")
plt.title("Average 24h weight cycle across all mice\n(Mean ± SEM)")
plt.xlim(0, 24)
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()